Blog
What is a Tablet Presser and How Does it Work?
A Tablet Presser is an essential machine in the pharmaceutical industry. It compresses powders into solid tablets, ensuring they have the correct shape and dosage. This process is crucial for producing medications that are safe and effective for consumers. With precise engineering, the Tablet Presser uses pressure to form tablets quickly and consistently.
The operation of a Tablet Presser involves multiple stages. Powders are first fed into a die, where they are subjected to high pressure. This pressure binds the particles together, creating a solid mass. The machine then ejects the finished tablets, ready for packaging and distribution.
Despite its effectiveness, the Tablet Presser does have some limitations. Variations in powder consistency can affect tablet quality. Operators must monitor machinery to ensure optimal performance. This process requires careful attention and sometimes multiple adjustments. Users must remain aware of these challenges to maintain product integrity and safety.

What is a Tablet Presser?
A tablet presser is a machine used in manufacturing tablets. Its primary function is to compress powdered materials into solid doses. This process is essential in various industries, especially pharmaceuticals. Various components make up a tablet presser, including dies, punches, and a hydraulic system.
The die holds the powder in place. The punches apply pressure to form the tablets. As the punches descend, they compact the material. Once the tablets are formed, the presser ejects them for further processing. It's a precise operation that demands attention to detail. Common issues include uneven tablet density and broken tablets. Monitoring the process is crucial to avoid these pitfalls.
Tips: Always check the material's flowability before starting production. It can affect the tablet quality. Additionally, regular maintenance of the tablet presser will ensure consistent performance. Remember, small adjustments can lead to better outcomes.
The Components of a Tablet Presser
A tablet presser is a complex machine that compresses powdered materials into tablets. It is commonly used in pharmaceuticals and nutritional supplements. Understanding its components is essential to grasping how it operates effectively.
The main parts of a tablet presser include the feeder, die, and punches. The feeder supplies the powder, ensuring a uniform flow into the die. It's crucial that the powder is consistent. An inconsistent powder could lead to defects in the final product. The die shapes the tablet, while the punches apply pressure. These components work together to form solid tablets.
However, not all tablet pressers work the same way. Some may have advanced controls for precision, while others might be more basic. The settings can impact the tablet's hardness and dissolution rate. This variability can be frustrating for operators who seek perfection. Regular maintenance is key to keep the machine running smoothly, but even with maintenance, problems can arise. Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting common issues, but it doesn't guarantee flawless results every time.
Tablet Pressing Efficiency Over Various Pressures
The Working Mechanism of a Tablet Presser
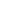
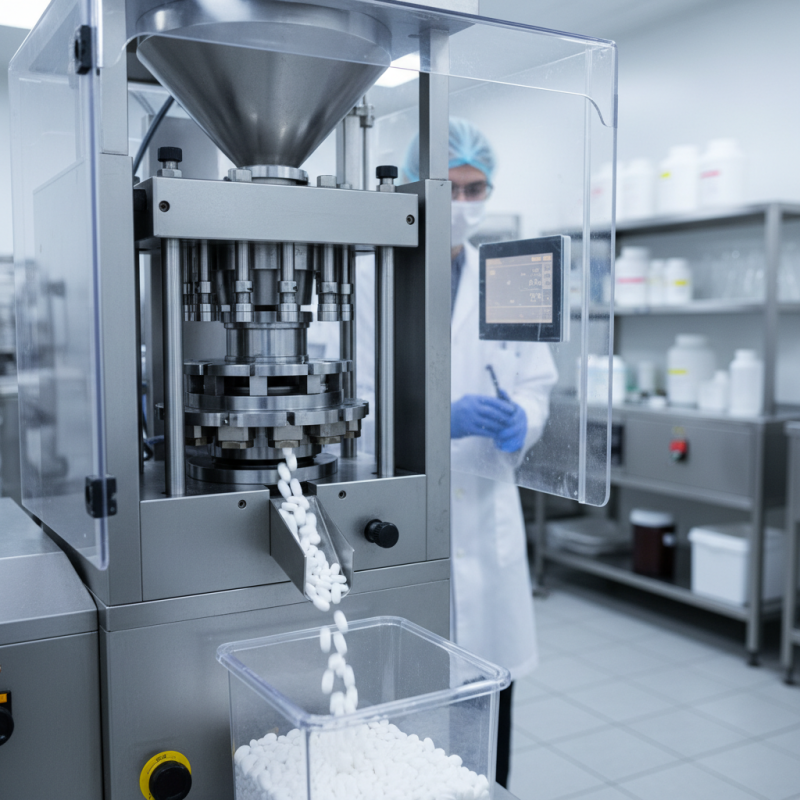
A tablet presser is an essential machine in the pharmaceutical industry. It is designed to compress powder into tablets efficiently. The working mechanism of a tablet presser involves several intricate components. The process begins with powder feeding into a die cavity. A punch then applies pressure, forming a solid tablet. The force applied can reach up to 100 tons, depending on the material and required tablet density.
During the compression phase, uniformity is crucial. Inconsistent powder density can lead to uneven tablets. Professionals must ensure that the powder flow is smooth and uniform. Using a tablet presser with adjustable settings can also improve the quality of the end product. This adaptability allows for various tablet sizes and shapes.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance of the tablet press can prevent malfunctions. Inspecting the punches and dies every week can save time and resources. Additionally, conducting trials with different formulations can help identify the perfect blend for optimal tablet formation. Inconsistent results can often disrupt production schedules. Continuous monitoring is key to efficiency.
Applications of Tablet Pressers in Industry
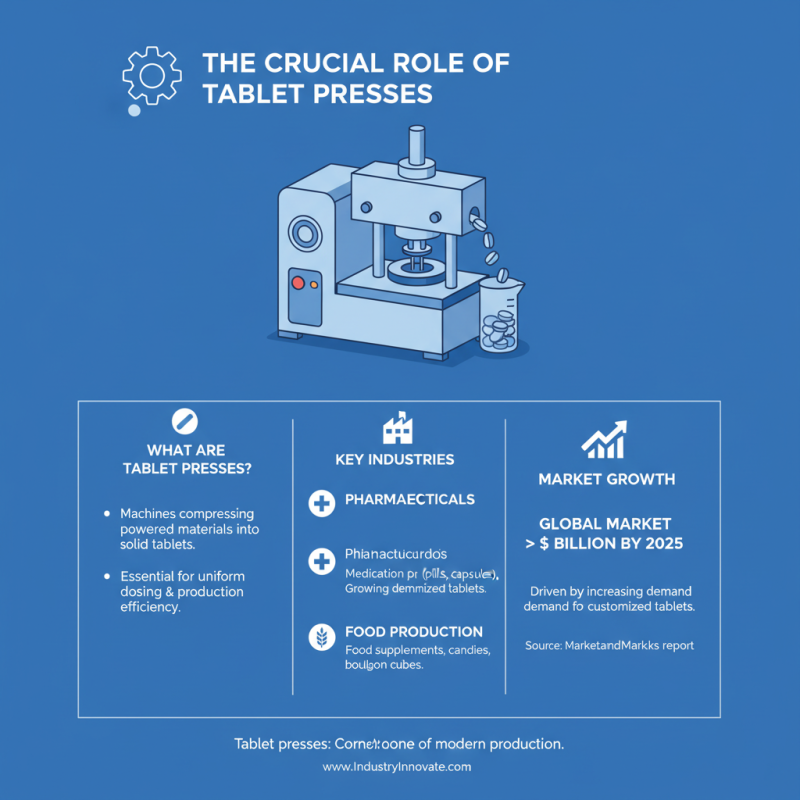
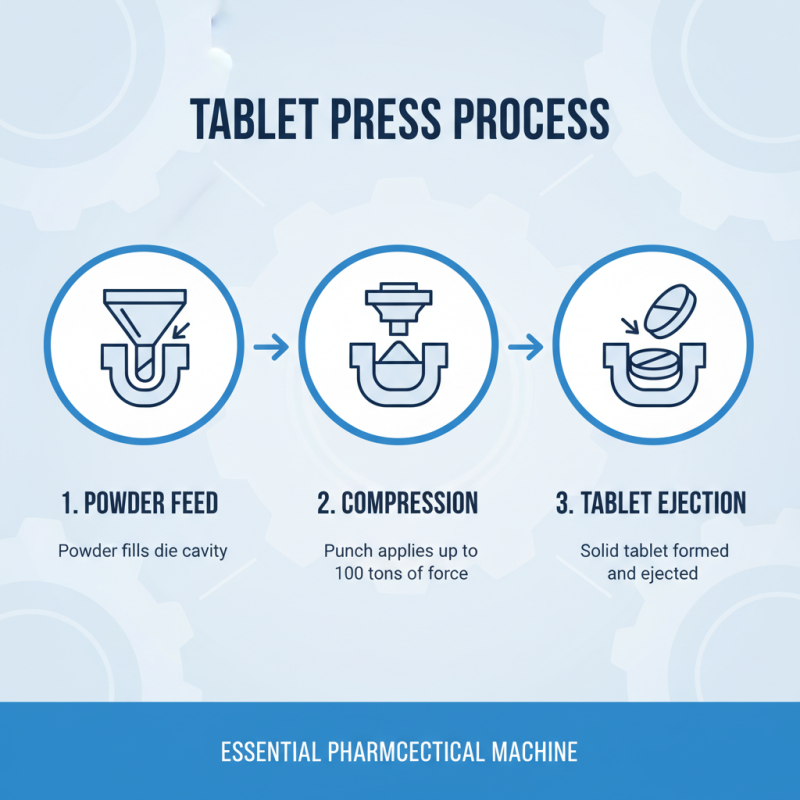
Tablet pressers play a crucial role in various industries, especially in pharmaceuticals and food production. They are vital for compressing powdered materials into solid tablets. In the pharmaceutical sector, tablet pressers help to produce a wide range of medications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global tablet press market is projected to exceed $1 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for customized tablets.
In food production, tablet pressers are used to manufacture dietary supplements and functional foods. These machines ensure uniformity and consistency in tablet size and dosage. For instance, a study published in the International Journal of Food Science found that tablet pressers can improve the bioavailability of nutrients, enhancing their effectiveness. However, operators must remain cautious. Improper calibration can lead to inconsistencies, affecting product quality.
Moreover, the environmental impact of tablet pressing should not be overlooked. Many manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials to minimize waste. Reports suggest that the industry is moving towards sustainable practices. Nevertheless, challenges remain. Many companies struggle to balance efficiency and environmental responsibility. The quest for innovation continues, highlighting the ongoing need for industry-wide reflection and improvement.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Tablet Pressers
Tablet pressers are vital in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They compress powders into tablets. Proper maintenance and safety protocols are crucial for their efficiency. Poorly maintained equipment can lead to production failures.
Regular cleaning is essential. Dust and residue can affect the quality of tablets. Schedule daily cleanings, especially after product changes. Use appropriate solvents for different materials. Dust can accumulate quickly. A small maintenance oversight can lead to larger issues.
Training staff is equally important. Ensure everyone understands the machine’s operation. Accidents often stem from improper use. Implement a safety checklist. This should include checking for loose parts and ensuring emergency stops are functional. According to industry studies, 40% of tablet press malfunctions are due to operator errors. Always prioritize safety training sessions.
Tip: Use a routine maintenance log. Track service dates and issues encountered. This document aids in understanding equipment longevity. Remember, even minor parts should be inspected regularly. A proactive approach can save time and resources in the long run.
What is a Tablet Presser and How Does it Work? - Maintenance and Safety Tips for Tablet Pressers
| Feature | Description | Safety Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Force | The force used to compress powder into tablets, typically measured in tons. | Always verify the pressure settings before operation. |
| Die and Punch | Components that shape the tablet during compression. | Inspect dies and punches regularly for wear and replace as necessary. |
| Filling System | The mechanism that controls the amount of powder fed into the die. | Ensure proper calibration to avoid over or underfilling. |
| Lubrication | Use of lubricant to reduce friction during the compression process. | Use appropriate lubricants that do not affect tablet quality. |
| Operation Modes | Manual or automatic settings for controlling tablet production. | Train operators on proper use of the machine in all modes. |
| Cleaning Procedures | Routine cleaning to prevent contamination and ensure product integrity. | Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for cleaning processes. |
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Tablet Presser Efficiency with Data Driven Insights on Compression Techniques
-

A Comprehensive Guide to the Best Tablet Presses for Global Buyers
-

How to Choose the Right Tablets Press Machine for Your Production Needs
-

Why Choose Natoli Tablet Press for Your Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Needs
-

How to Optimize Your Production Efficiency with a Tablet Presser for Maximum Yield
-

Mastering Natoli Tablet Press Techniques for Optimal Performance