Blog
What is a Fluidized Bed Processor and How Does It Work for Efficient Material Processing?
In recent years, the demand for efficient material processing has surged across multiple industries, leading to the increased adoption of advanced technologies such as the Fluidized Bed Processor. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global market for fluidized bed systems is projected to grow from USD 6.8 billion in 2020 to USD 9.1 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1%. This growth underscores the importance of leveraging innovative processing techniques to meet production demands while enhancing efficiency.

A Fluidized Bed Processor operates on the principle of fluidization, whereby solid particles are suspended and agitated by a flowing gas or liquid. This process not only improves heat and mass transfer efficiency but also enables uniform processing of various materials, making it a versatile solution for industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and environmental applications. The increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing processes further drives the adoption of fluidized bed technology, positioning it as a key player in achieving operational excellence.
Moreover, industry-specific reports highlight that the ability of Fluidized Bed Processors to minimize thermal degradation and achieve a more uniform particle size distribution significantly contributes to product quality and consistency. As businesses seek to optimize their operations and reduce waste, understanding the functionality and advantages of Fluidized Bed Processors becomes crucial for achieving competitive advantages in the market.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Fluidized Bed Processors in Material Engineering

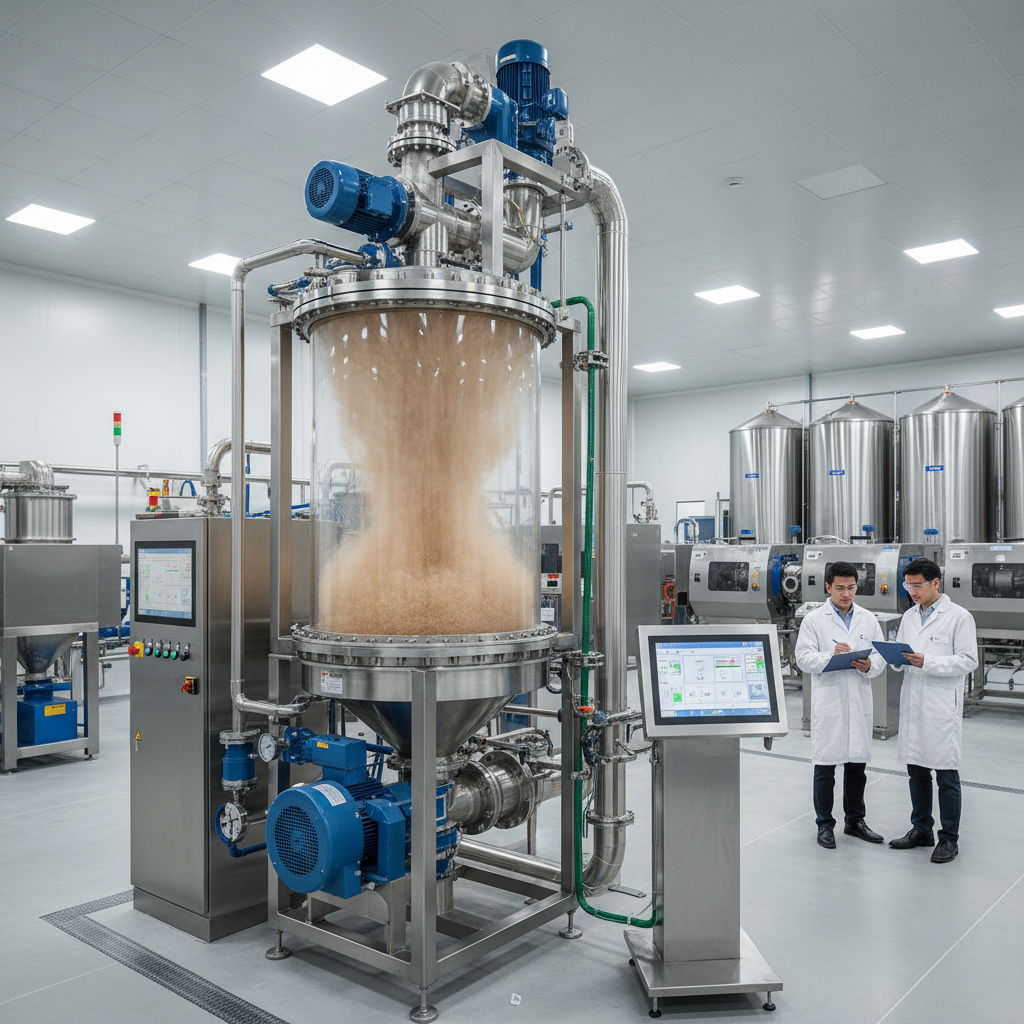
Fluidized bed processors are essential equipment in material engineering, primarily utilized for their ability to enhance processing efficiency through the principles of fluidization. The fundamental concept behind a fluidized bed lies in the suspension of solid particles in a flowing gas or liquid, which transforms the bed of solids into a fluid-like state. This behavior is achieved by introducing a gas or liquid at the bottom of a column containing granular material. As the velocity of the incoming fluid increases, the particles experience a balance of gravitational and drag forces, enabling them to behave like a fluid, allowing for improved mixing, heat transfer, and reaction rates.
The efficiency of fluidized bed processors is attributed to their ability to maintain uniform temperature and concentration throughout the processing chamber. This uniformity is critical when processing heat-sensitive materials or conducting chemical reactions that require precise control. Additionally, the continuous nature of fluidized bed operations allows for extended contact time between solid and fluid phases, enhancing the effectiveness of processes such as drying, granulation, and coating. By optimizing parameters such as particle size, fluid velocity, and temperature, engineers can tailor fluidized bed designs to meet specific processing requirements across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and materials development.
Key Applications of Fluidized Bed Processing Across Various Industries
Fluidized bed processing has become a crucial technology across various industries, offering efficient material handling and processing capabilities. This technique utilizes a flow of air or gas to suspend solid particles, creating a fluid-like state that enhances mixing, heat transfer, and reaction efficiency. Key applications of fluidized bed processing can be found in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing, where uniform heating and consistent material properties are essential for product quality.
In the pharmaceutical industry, fluidized bed processors play a vital role in granulation and coating processes, allowing for the creation of uniform pellets crucial for drug formulation. Meanwhile, in food processing, they are utilized for drying, roasting, and coating operations, ensuring consistent texture and flavor in products.
Moreover, the chemical sector benefits from fluidized bed reactors for catalytic processes, maximizing reaction efficiency while minimizing energy consumption.
As industries increasingly recognize the advantages of fluidized bed technology, the global fluidized bed boiler market is projected to grow significantly, from $984.22 million in 2025 to $1.26389 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 3.64%.
The Mechanism of Fluidization: How Particles Achieve Suspension and Motion
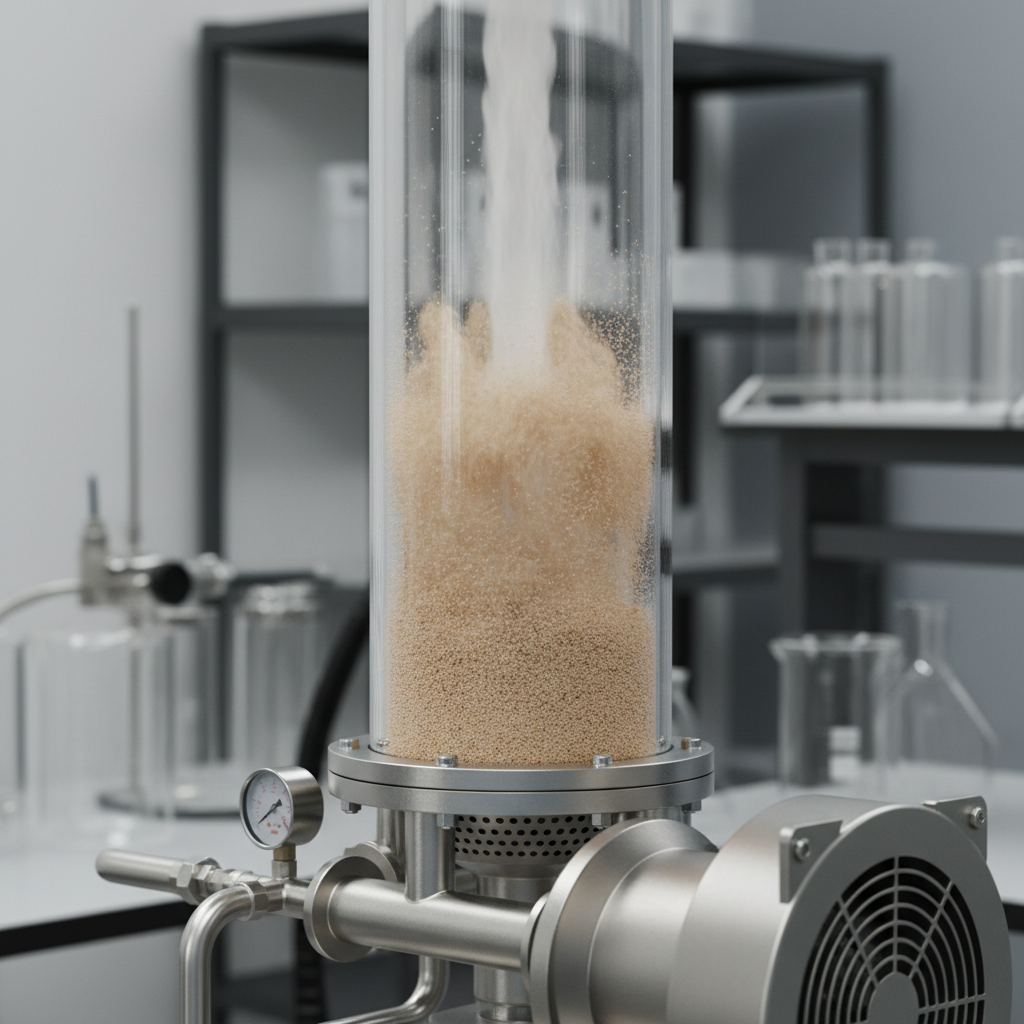
Fluidized bed processors utilize the principle of fluidization, whereby solid particles are suspended in a flowing fluid, typically air or gas. This process begins when air is introduced through a perforated distributor plate at the bottom of the bed, creating an upward flow. As the fluid velocity increases, the gravitational forces acting on the particles are counteracted, leading to a condition where the particles no longer rest on the bed but are suspended in the fluid. This phenomenon enhances heat and mass transfer, as the particles move freely, resulting in more efficient processing.
The key to achieving effective fluidization lies in the balance between the forces acting on the particles. Initially, as the fluid velocity increases, particles experience a drag force from the fluid. When this drag force exceeds the weight of the particles, they become suspended. Proper fluidization is crucial; if the velocity is too low, particles remain at rest, while excessive velocity can lead to "defluidization," where particles escape the bed or form bubbles. Achieving optimal conditions allows for uniform mixing, effective heat transfer, and efficient chemical reactions, making fluidized bed processors widely used across industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and materials science.
What is a Fluidized Bed Processor and How Does It Work for Efficient Material Processing?
| Parameter | Description | Value/Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fluidizing Velocity | Velocity at which particles are suspended in the fluidized bed | 0.1 - 1 m/s |
| Particle Size | Diameter of particles suitable for fluidization | 50 - 1000 µm |
| Bed Height | Height of the fluidized bed during operation | 0.5 - 2 m |
| Production Capacity | Amount of material processed in a specific time frame | 100 - 5000 kg/h |
| Temperature Range | Operating temperature of the fluidized bed | 20 - 500 °C |
Comparative Analysis: Fluidized Bed Processing vs. Traditional Processing Methods

Fluidized bed processing distinguishes itself from traditional methods through its unique mechanism of operation. In fluidized bed systems, solid particles are suspended in a gas or liquid stream, creating a dynamically enhanced environment that improves heat and mass transfer. This results in uniform temperature distribution, minimized thermal gradients, and improved reaction kinetics, making fluidized beds particularly suitable for processes such as drying, granulation, and coating. In contrast, traditional processing methods often rely on static conditions, which can lead to uneven heating and localized hot spots, ultimately reducing efficiency.
Moreover, fluidized bed processing offers greater scalability and flexibility compared to conventional approaches. While traditional methods may require specific equipment adjustments for different batch sizes, fluidized beds can seamlessly accommodate varying scales without significant modifications. This adaptability allows for continuous processes and easier integration into automated production lines. Furthermore, the reduced energy consumption and shorter processing times associated with fluidized bed systems enhance overall productivity, providing a compelling advantage over traditional techniques in various industrial applications.
Efficiency Metrics: Measuring the Performance of Fluidized Bed Processors in Operations
Fluidized bed processors have become a cornerstone of material processing in various industries due to their efficiency and effectiveness. To quantify this efficiency, operators often rely on several key performance metrics. One critical metric is the minimum fluidization velocity, which indicates the air or gas flow required to suspend particles in the bed. According to industry reports, achieving optimal fluidization can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, making processes more sustainable and cost-effective.
Another essential metric is the residence time distribution (RTD) of particles within the bed. A study published by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers found that processors demonstrating an RTD close to the ideal model achieved a 15% increase in output quality. This highlights how effectively managing the particles' residence time can enhance the processing performance, leading to uniform product characteristics and reduced waste.
Moreover, the scalability of fluidized bed processors is also a pivotal performance indicator. Research shows that when scaled properly, these systems maintain efficiency, with larger units demonstrating only a 10-15% decrease in fluidization effectiveness compared to their smaller counterparts. This scalability ensures that operational efficiency is preserved, allowing for seamless expansion in production without compromising on performance metrics.
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Fluidized Bed Processors for Efficient Material Processing
-

Understanding the Role of Fluidized Bed Processors in Modern Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
-

How to Optimize Tablet Presser Efficiency with Data Driven Insights on Compression Techniques
-

Top 5 Oral Dispersible Tablets for 2025 That You Need to Know About
-

7 Best Features of Syringe Assembly Machines for Optimal Production Efficiency
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Capsule Loader Machine for Your Business Needs